This guide is intended for managers and employees of companies involved in organizing business visits and employing foreigners from distant countries in Russia. The text is simplified to help you spend a minimum amount of time understanding the basic aspects of business migration, to effectively organize this process in your company, and to minimize associated risks.
The entry of foreign citizens into Russia is often associated with a lot of difficulties. Document processing for entry involves numerous bureaucratic procedures, immigration legislation often changes and is applied ambiguously by authorities. When foreign visitors are invited by a company, there are often disputes with government agencies.
To obtain documents for entry into Russia, it is necessary to go through the control of several state authorities where data is checked, both of the foreigner and the inviting company. At the same time, no Russian migration law should be violated, the responsibility for which is serious up to the suspension of the company's activities, criminal punishment, and deportation of foreign citizens from Russia. Even a violation of migration laws due to ignorance or carelessness can lead to serious financial and legal risks, and the shutdown of the entire business.
To avoid risks associated with business migration, it is important to be able to promptly, legally, and professionally resolve any disputed situations that arise. To do this, it is crucial to seek the support of professionals with significant experience in this field who are capable of competent interaction with government officials and resolving complex issues.
This guide describes the mandatory procedures that need to be followed for a business visit or employment of foreign citizens in Russia, including their entry, stay, and exit from the Russian territory. You will also learn about the responsibility for violating Russian migration laws, how to avoid it, and other useful information for you.
By studying this guide, you will understand how all processes of business migration in Russia are organized. The text is divided into the main procedures and questions related to business migration. You can use it as a desktop reference when structuring and controlling these processes in your company, as well as when interacting with your partners in the field of migration.
- Entering Russia formalities
- What types of Russian work and business visas exist?
- Who can be invited to Russia for a business visit?
- Who can be employed in Russia from far abroad?
- How to obtain a business or work visa? General rules for obtaining business and work visas
- Features of obtaining a business visa
- Features of obtaining a work visa
- How to obtain a work visa for a highly qualified specialist?
- How to obtain a work visa for a regular foreign employee (non-highly qualified specialist)?
- Entry, stay and exit from the territory of Russia. What needs to be done upon entry into Russia?
- What to consider for foreign citizens in Russia?
- What foreigners need to consider when leaving Russia?
- Responsibility for violation of migration laws in Russia
- What administrative responsibility is provided for a company, its management, and employees?
- What administrative responsibility is provided for a foreign citizen?
- What is the criminal liability for violation of migration laws in Russia?
- How to avoid liability for violating migration laws in Russia?
- Risks of Business Migration to Russia
- State regulation of migration in special situations
- What is Russia's migration policy? What are its goals?
- What are the main laws regulating business migration in Russia?
- Resume
Entering Russia formalities

You will learn:
1. What documents are required for entering Russia for a business visit or work?
2. Who is involved in the process of arranging entry for foreign citizens into Russia?
3. Which countries have simplified entry procedures or a visa-free regime with Russia?
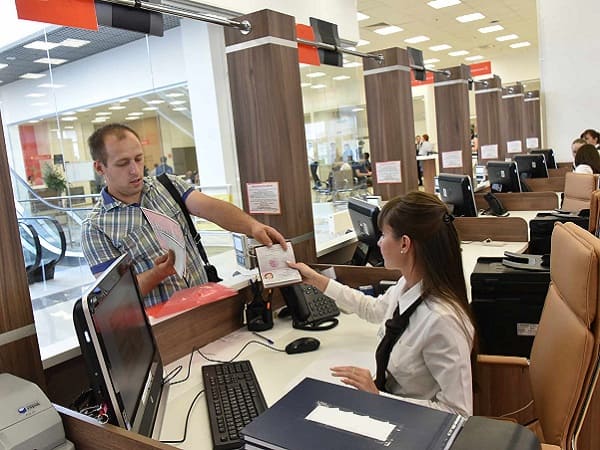
Most often, as part of their business activities, companies invite foreign citizens to Russia for employment or business visits.
To travel to Russia on a business trip, a foreigner needs to obtain a business visa, for which the company must issue an invitation. If a foreigner comes to Russia for work, he or she needs to obtain a work visa, for which in addition to an invitation, it is also necessary to obtain a work permit.
During the process of arranging documents for the entry of a foreign citizen into Russia, there are three parties involved: (i) the inviting party, (ii) the foreign citizen themselves, and (iii) government agencies. The inviting party is a Russian company (hereinafter referred to as "the Company") that invites the foreign citizen.
IMPORTANT: The inviting party for a business visa can be either the Company itself or another legal entity, a migration service provider, engaged by the Company to organize business migration within its projects. In this case, the receiving party in the invitation and the business visa is not the Company itself, but such a legal entity. However, certain requirements must be met to avoid risks associated with formal violations of migration legislation, which will be described in other sections of this guide.
For a work visa, only the Company itself can act as the inviting party.
As mentioned earlier, when preparing documents for entry, several government agencies must be checked, at least: (i) the migration service (one of the units of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia), (ii) the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, and (iii) the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB). The data of both the foreign citizen (credibility, involvement in crimes or violations of Russian laws in the past, etc.) and the inviting company (constituent documents, information about activities, and the presence of violations in the field of migration laws) are verified. At each stage of the check, the foreign citizen may be denied entry.
Russian consulates located in the country where the foreigner is obtaining the visa are also involved in the process of obtaining entry documents. The consulate receives the foreigner's application for a business or work visa, and then issues the visa or may refuse to issue it for various reasons.
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia establishes a list of migration-risky countries (whose citizens more often than others violate the legislation of Russia). The list includes a large number of countries (for example: Iran, Vietnam, China). The documents of citizens from such countries are subject to more thorough verification and often take longer than usual.
Russia has a visa-free regime with some countries. The visa-free regime is only for tourism and visiting relatives, not for work or business purposes (for example: Peru, Cuba, Turkey).
Foreigners from neighboring countries also have simplified procedures for entering and getting employed in Russia. The complexity of such procedures varies depending on the agreement with each country (for example, citizens of the Republic of Belarus can enter Russia with their internal passport and do not need to apply for a migration card).
Countries of the former Soviet Union that are now part of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) but not members of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) are considered as neighboring countries for Russia (for example, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan), and their citizens can enter Russia using a foreign passport. Other countries are considered as distant foreign countries.
With an initially professional approach, business migration to Russia can be carried out without any problems or additional efforts. However, in practice, especially in the context of large projects, situations often arise that require special attention and an individual approach for their successful resolution.
It should be noted that the consulate reserves the right to refuse to issue a visa to an applicant if there are serious grounds for doing so. In case of refusal to issue a visa, the paid fee is non-refundable.
Summary:
1. To enter Russia for business or work purposes, a business or work visa is required, respectively.
2. To obtain any of the mentioned visas, an invitation to enter Russia must be obtained first.
3. In addition to the invitation, a work permit must be obtained to obtain a work visa.
4. At least the inviting party, the foreign citizen, the Migration Department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia (migration service), the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, and the Federal Security Service of Russia are involved in the entry process to Russia.
5. Russia has a visa-free regime with some countries (e.g., Peru, Cuba, Turkey).
6. Simplified entry and employment procedures apply to foreigners from neighboring countries in Russia.
...
What types of Russian work and business visas exist?

You will learn:
1. What are the parameters of visas for business and work travel to Russia?
2. What are the requirements for an foreigner's passport to obtain a Russian visa?
3. How many days can a foreigner stay in Russia on a business visa (the 90/180 rule)?
4. What should be considered when choosing a visa with certain parameters?
For entry to Russia for work or on a business visit, foreigners are issued regular work or business visas, respectively, which have several parameters.
These parameters include:
TYPE OF VISA
- business
- work
There are other types of visas, such as tourist, private, student, etc., but they are not related to business trips and work, which are discussed in this guide.
VISA CATEGORY
Work and business visas belong to the category of "ordinary" visas.
There are also other categories of visas, such as official, diplomatic, transit, etc., but business and work visas are not among them.
PERIOD OF VISA VALIDITY
- up to 3 months;
- up to 12 months;
- up to 3 years (for highly qualified foreign specialists).
When determining the duration of a visa, the validity period of the foreign citizen's passport is also taken into account. The passport must be valid for another 6 months after the intended date of departure from Russia (i.e. the date of visa expiration). For example, if the passport expires on December 10 of the current year, a visa may be issued to a foreign citizen for a period not exceeding June 10 of the same year. The duration of the visa is indicated in the invitation issued to the foreign citizen.
When applying for a work visa, the validity of the foreign worker's passport (non Highly qualified foreign specialists) must be at least 1.5 years from the date of the visa's start of validity.
It should be noted that the 90/180 rule applies to a business visa. A foreigner who arrives in Russia on a business visa cannot stay on Russian territory for more than 90 days within a 180-day period. This means the following:
- after the first day of entry into Russia, the countdown of 180 days begins.
- within these 180 days, a foreigner can stay in Russia for only 90 consecutive or cumulative days. During these 90 days, they can cross the border multiple times on a multiple-entry visa.
- upon reaching 90 days of stay in Russia, the foreign national must leave Russia and will not be able to enter again until the expiration of 180 days from the date of the first entry. In some cases, this restriction can be overcome by obtaining another visa, which will start a new 90-day period for stay in Russia.
Regarding work visas, the 90/180 rule does not apply.
VISA MULTIPLE ENTRY
The multiple entry visa determines how many times a foreigner can enter Russia on that visa. Depending on the entry type, work and business visas can be classified as:
- single-entry or double-entry: with such visas, a foreigner can enter Russia once or twice, respectively. These visas are issued for a period of up to 3 months;
- multiple-entry visas allow the foreigner to enter Russia an unlimited number of times. Such visas are issued for a period of up to 12 months, and up to 3 years for highly qualified foreign specialists.
In most cases, a single-entry or double-entry business visa for 3 months is obtained for the first visit to Russia. In certain cases, it is possible to obtain a multiple-entry visa for a period of more than 3 months, but it is necessary to justify this need to the migration service when applying for an invitation for the foreigner to enter Russia.
If an ordinary foreign worker obtains a work visa, they are first issued a single-entry visa for a period of 3 months. This is necessary so that the foreign worker can enter Russia for the first time to receive a ready-made work permit. Then, such a visa is reissued as a multiple-entry visa for a period of 1 year. Highly qualified foreign specialists (HQFS) are granted a work visa for 3 years immediately.
TRAVEL PURPOSES FOR VISA
In business and work visas, the purpose of the trip is indicated for which the foreigner is coming to Russia. In total, there are 14 such purposes for business visas and 6 for work visas. More details on the purposes of trips on visas are considered below.
The parameters of a visa vary depending on the purpose and the required length of stay of the foreign citizen in Russia.
Experience shows that the shorter the requested visa period, the easier it is for a foreign citizen to obtain it, especially if they are visiting Russia for the first time. When applying for a subsequent visa, if the foreign citizen did not violate any rules during their first visit, a multiple-entry visa for a longer period may be issued.
The migration service always carefully checks the validity of the stated parameters in the invitation documents, especially in the case of large projects requiring the issuance of a large number of business or work visas. In such cases, not only each foreign citizen is checked, but also the reputation of the company (its type of activity, history of issuing invitations in the past, etc.), its activities, and circumstances under which the foreigner needs to visit Russia. Usually, such a check requires negotiations with the migration service and preparation of supporting documents.
As for work visas, they are multiple-entry and issued for the validity period of the work permit. However, an ordinary foreign worker is first issued a single-entry visa for a period of 3 months. This is necessary so that the foreigner can enter Russia on it after obtaining a work permit. Once in Russia, this visa is reissued as a multiple-entry one. Highly qualified foreign specialists (HQFS) receive a work visa for 3 years immediately.
It is important to have a clear understanding of the purpose, duration, and necessity of the foreigner's visit to Russia when choosing visa parameters. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a visa with appropriate duration, validity, and travel purposes. It is crucial that the stated travel purposes in the invitation and visa reflect the true purpose of the visit to Russia, as providing false information about the purpose of the visit (for example, stating a business purpose when the foreigner is actually coming to work) may result in serious legal consequences for violating migration legislation.
To obtain a Russian visa, it is possible to apply at Russian consulates located in various countries around the world. In order to apply for a visa to Russia, a foreigner must present an invitation to visit Russia that has been issued for them by the inviting party. The inviting party can be a private individual, organization or state.
Summary:
1. Parameters of business and work visas:
|
Type |
Category |
Purpose of the trip |
Multiplicity |
Duration |
|
Business |
Ordinary |
14 types of travel purposes: 1. Business 2. Commercial 3. Driver 4. Crew member 5. Technical maintenance 6. Business trip for media 7. Negotiations 8. Receiver 9. Medical treatment 10. Adoption 11. Lecturer 12. Press/correspondent 13. Press/technical staff 14. Accompanying family member |
1. Single-entry, double-entry |
up to 3 months |
|
2. Multiple-entry |
up to 12 months |
|||
|
Work-related |
Ordinary |
6 types of travel purposes: 1. Employment 2. Foreign employee 3. Teacher 4. Correspondent 5. Technical staff 6. Accompanying family member |
1. Single entry. |
up to 3 months |
|
2. Multiple-entry. |
up to 12 months |
|||
|
3. For Highly qualified foreign specialists - multiple entry |
Up to 3 years |
2. When obtaining a work visa, the foreigner's passport must be valid for another 1.5 years from the start date of the visa, and for business visas, another 6 months after the planned end date of the visa.
3. A foreign national cannot stay in Russia on a business visa for more than 90 days within a 180-day period.
4. When choosing a visa, it is necessary to clearly determine the required parameters based on what may need to be justified to the migration service. Any discrepancies between the visa parameters and the actual stay of a foreigner in Russia may lead to a formal violation of migration legislation and significant legal and financial risks.
...
Who can be invited to Russia for a business visit?

You will learn:
1. Who can enter Russia on a business visa?
2. How many purposes of entry to Russia on a business visa exist?
3. What are the most common purposes of entry used?
A company can invite any foreign citizen for a business visit, provided that their entry into Russia is not prohibited. The business trip of such a foreigner must be necessary within the framework of the company's commercial activities in Russia. To undertake such a trip, the foreigner needs to obtain a business visa.
Russian legislation provides for 14 possible purposes of travel, which are indicated in the business visa.
MOST COMMON PURPOSES OF ENTRY TO RUSSIA:
Business - for foreigners visiting government and commercial organizations to participate in negotiations (consultations, conferences), as well as for the purpose of improving qualifications or professional retraining.
Commercial - for foreigners visiting commercial organizations to solve business issues (conducting commercial negotiations, concluding contracts, etc.), as well as for participation in exhibitions and other events with a commercial character.
For such trips, it is possible to obtain (i) a single or double-entry visa for up to 3 months, or (ii) a multiple-entry visa for up to 12 months.
It can be said that the business purpose of entry is used when visiting Russia to search for and meet with business partners, study the market for goods and services, participate in negotiations, conferences. The commercial purpose of entry is used for visits to conclude and extend contracts, participate in exhibitions, and solve strictly commercial issues.
Other purposes of entry when applying for a business visa are used less frequently. These include:
|
- Driver - Crew member - Technical maintenance - Business trip for media representatives |
- For such trips, (i) a single or double entry visa valid for up to 3 months, or (ii) a multiple entry visa valid for up to 12 months can be issued. |
|
- Negotiations - Recipient - Medical treatment - Adoption - Lecturer - Press/correspondent - Press/technical staff |
- For such trips, a single or double-entry visa valid for up to 3 months may be issued |
|
- Accompanying family member |
- For such a trip, a visa can be issued for the duration of the accompanying family member's visa |
IMPORTANT:
There are conflicts in Russian legislation regarding the definition of some statuses of foreigners for business visas, such as "crew members" or "technical maintenance". For example, in practice, there is a position of migration service employees according to which workers, for instance, of a floating fish processing base, who provide fish processing and harvesting directly on the vessel, may be classified not as crew members but as regular workers engaged in labor activities on Russian territory. According to this position, such workers are required to obtain a work permit in Russia and a work visa, not a business visa.
Similar controversial situations are usually resolved, but to do so, they need to be individually regulated with migration service employees for each company project involving the entry of such foreigners on a business visa.
Visiting Russia on business visas is a fairly common practice, and obtaining such visits is much easier than obtaining work visas and employing foreign citizens in Russia. Such trips are suitable for short-term visits of foreigners when their presence is necessary to resolve business issues arising within the Company's activities.
A business visa to Russia is a sticker in the passport. It should contain information about the validity and number of entries, the purpose of the foreign citizen's trip, their passport details, as well as information about the inviting party.
Resume:
1. Any foreign citizen who is not prohibited from entering Russia can enter on a business visa.
2. There are 14 purposes of entry to Russia on a business visa.
3. The most common purposes for entry to Russia on a business visa are "business" and "commercial".
...
Who can be employed in Russia from far abroad?

You will learn:
1. Who can enter Russia on a work visa from far abroad?
2. How many purposes of entry to Russia on a work visa exist?
3. Which purpose of entry is used most frequently?
4. What categories of foreign specialists does Russian migration legislation divide into?
5. Pros and cons of issuing visas for different types of foreign workers entering Russia.
A company can hire any foreign citizen who is not prohibited from entering Russia. To work in Russia, a foreigner from a distant foreign country needs to obtain a work permit and a work visa. Russian legislation provides for 6 possible purposes of travel, which are specified in the work visa.
Usually, work visas are issued with the purpose of "employment". For such purposes, a single-entry visa can be issued for up to 3 months. This visa is issued so that the worker can enter Russia after obtaining a work permit. Then, documents must be submitted to the migration service to obtain a multiple-entry visa for up to 12 months (the total period is calculated from the moment of entry into Russia on a single-entry visa but not exceeding the duration of the employment contract).
Work visas with other purposes of travel are used less often. These include:
|
- Foreign employee - Teacher - Correspondent - Technical employee |
- For such trips, a single-entry visa valid for up to 3 months can be issued. Later, this visa can be replaced with a multiple-entry visa valid for up to 12 months (the total duration is calculated from the moment of entry into Russia on a single-entry visa). |
|
- Accompanying family member |
- A visa for the duration of the accompanying family member's visa may be issued for such a trip. |
There are two categories of foreign workers who can be employed in Russia from countries outside the former Soviet Union:
Highly Qualified Specialists (hereinafter "HQS") are foreign workers who have work experience or skills in the field for which they are hired by the company. Their salary must be at least 167,000 rubles per month (there are exceptions for workers in science, medicine, education, Skolkovo Innovation Center, Republic of Crimea, and the city of Sevastopol).
HQS are immediately issued a multiple-entry work visa for "employment." The visa is issued for the term of the employment contract with the foreigner, but not more than three years. Such a visa can be repeatedly extended for the term of the employment contract, but not more than three years for each extension.
Ordinary foreign workers are foreign workers who do not fall under the category of HQS, and whose salary is less than 167,000 rubles per month.
Such workers are issued a single-entry work visa for "employment." Initially, the visa is issued for a period of up to 3 months. Then, documents must be submitted to the migration service to extend the stay and obtain a multiple-entry visa for up to 12 months (the total duration is calculated from the moment of entry into Russia on a single-entry visa, but not exceeding the duration of the employment contract).
When choosing a category for a foreign worker that the company wishes to employ, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of both categories. The process of employing an HQS is simpler, faster, and less expensive compared to employing an ordinary worker. However, HQS have a high minimum salary requirement, and not every worker can be employed as an HQS. It is advisable for companies to confirm the high qualifications of HQS with some documents (e.g., a diploma in the relevant profession).
Detailed procedures for employing HQS and ordinary workers and their differences are further discussed below.
It is worth noting that if you comply with all the rules of employment of foreign citizens and have a complete set of documents, you can legally work in Russia without fear of deportation, fines or entry bans. Also, until June 15, 2021, foreign citizens do not need to extend their temporary stay documents in Russia or register their place of residence.
Summary:
1. Any foreign citizen from a distant country who is officially employed in Russia and is not prohibited from entering the country can enter Russia on a work visa.
2. There are a total of 6 purposes for entry into Russia on a work visa.
3. The most common purpose for entering Russia on a work visa is "employment".
4. There are two categories of foreign workers in Russia who can be hired from distant countries: (i) highly qualified specialists (HQS) and (ii) ordinary foreign workers.
5. Pros and cons of applying for entry into Russia for different categories of foreign workers:
|
Categories |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Highly qualified specialists |
1. The process of obtaining work permits is simpler, faster, and less expensive compared to ordinary workers. 2. There are no quotas on the number of foreign workers. |
1. High minimum salary. 2. Not every worker can be employed as a Highly Qualified Specialist, it is desirable to confirm high qualifications with some documents (such as a diploma). |
|
Ordinary foreign workers
|
1. Low minimum salary. 2. No need to confirm the employee's high qualifications. |
1. The process of employment is more complicated, lengthy, and costly for ordinary workers compared to HQS. 2. For certain positions, there are quotas set by the government for ordinary foreign workers, meaning only a limited number of such workers can be employed during the year. There are also positions for ordinary foreign workers where no quotas are set. |
...
How to obtain a business or work visa? General rules for obtaining business and work visas

You will learn:
1. Who issues business and work visas?
2. How to obtain an invitation for a business or work visa?
3. How to obtain a business or work visa?
4. What is an electronic visa (E-Visa)?
Business and work visas are issued by Russian consulates based on an invitation received by the foreign citizen from a company. In order to obtain a work visa, in addition to the invitation, the foreigner must have a work permit.
ISSUANCE OF INVITATION TO A FOREIGN CITIZEN
An invitation is issued by the migration department of the police (migration service), with the inviting party being indicated as the Company in the invitation. As mentioned earlier, for obtaining a business visa, another legal entity engaged by the Company to organize business migration within its projects may be indicated as the inviting party.
IMPORTANT: Considering the significant risks and nuances of regulating business migration, it is beneficial for Companies, especially for large projects, to engage a reliable partner - a provider of migration services. The partner engaged by the Company takes on all the obligations and responsibilities of the inviting party in relation to the invited foreign citizen. The direct risks associated with migration flows and violations of migration laws in Russia are transferred from the Company to such a partner. Such a partner can ensure all the work related to organizing migration flows for the Company and interaction with the migration service. This interaction with the engaged partner allows for more reliable legal protection and overall project effectiveness for the Company.
However, there are collisions in Russian legislation on this issue. Provisions of migration laws regarding the inviting party can be interpreted ambiguously. Often, migration service employees consider it impossible to appoint another legal entity as the inviting party for Company projects. Such a position asserts that only the Company can be the inviting party and must be indicated in both the invitation and the business visa issued to the foreigner.
In practice, this issue has to be resolved individually with immigration officials each time. All project details are crucial in making a decision on this matter. In particular, the immigration service pays close attention to large projects that involve a significant number of foreign nationals entering Russia.
It is essential for the Company's partner to be capable of professionally resolving such issues without any risks to the Company.
To issue an invitation to a foreign national, the Company must submit the appropriate request (application) to the migration service, along with the necessary documents. Prior to submitting such a request, the Company is also obliged to register with this police department.
The invitation can be issued on a special paper form or in electronic format. If the invitation is issued on paper, it must be sent to the foreign national in the country where they will obtain their visa. The foreign national must present this form at the Russian Consulate in that country when applying for a visa. The consulate and the country where the visa will be obtained are specified in the invitation itself.
If an invitation is issued in electronic form, the migration service independently sends it via email to the Russian consulate in the country where the visa will be obtained. The consulate is specified in the Company's application when the invitation is being processed. A copy of such an invitation is sent to the email address provided by the Company. The foreign citizen only needs to present this invitation in printed form when applying for a visa at the Russian consulate.
An invitation for a business visa with the purpose of entry "commercial" or "business" can also be issued on the Company's regular form. Such an invitation should be sent to the foreign citizen in the country where they will obtain the visa. The foreigner must then present the invitation at the Russian consulate in that country when applying for a visa.
However, as practice shows, obtaining a visa based on an invitation on the Company's form is possible only for a small number of requested visas (usually up to 10 people). Otherwise, consular officials may refuse to issue visas. In this situation, the consulate may require obtaining invitations from the migration service in order to conduct a comprehensive check of a large number of incoming foreigners. Accordingly, an invitation on the Company's form is suitable for a small number of business visits, provided that the consulate makes a positive decision to issue a visa based on such an invitation.
The deadline for processing an invitation by law is 20 business days. At the discretion of the leadership of the migration service, this period may be reduced. To shorten the term, it is necessary to substantiate in writing the need for expedited issuance of the invitation, however, the migration service does not always agree to expedite the issuance due to considering the justification insufficient or due to their workload. Usually, personal communication with the leadership of the migration service is required to expedite the issuance of the invitation, involving a professional partner of the Company who is capable of skillfully resolving the issue of expedited processing.
When issuing an invitation to a foreigner, the Company undertakes to provide them with medical assistance, necessary financial means, and accommodation in Russia. Providing false information to the Company about the purpose of the foreigner's visit to Russia (for example, indicating "business" or "commercial" as the purpose when in fact the foreigner is coming to work for the Company) will result in a fine of 45,000-50,000 rubles for officials and 400,000-500,000 rubles for the Company.
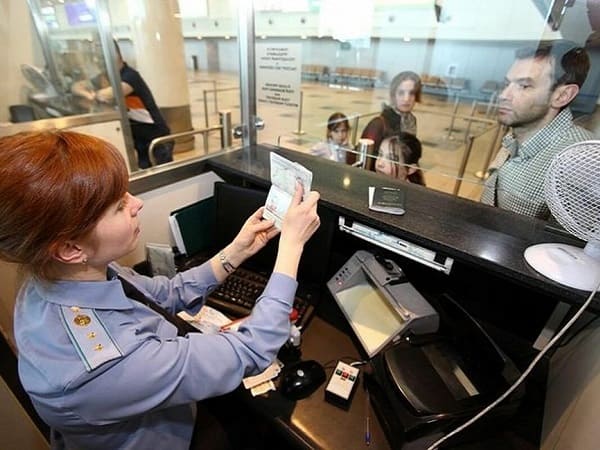
VISA APPLICATION
To apply for a visa, the foreign citizen must contact the Russian consulate located in the country where they will obtain the visa. The consulate issues a visa based on the parameters specified in the invitation to enter Russia provided to the foreigner. The foreign citizen or their representative must provide the following documents to the consulate:
- Passport
- Completed visa application form (available for download from the consulate's website)
- Invitation
- One photograph measuring 3.5 x 4.5 cm
- Documents showing payment of the consular fee
- Documents required depending on the type of visa (for example, a certificate (original and copy) showing the absence of HIV infection is required for work visas).
When submitting documents to the consulate, a receipt is issued indicating the date when the visa will be ready for pickup. This receipt must be presented when collecting the visa.
The decision on visa issuance is made within 16 days.
Please note that if you submit your visa application through visa centers, the processing time may be longer. Visa centers are not part of the consulate and the visa processing time is counted from the day the consulate receives the documents from the visa center. If you need to obtain the visa quickly, you should apply directly to the consulate.
The visa processing time also depends on the chosen tariff for consular services. Usually, the processing time can be shortened to one working day, but the consular fee will be significantly higher.
In case of visa denial, the consular fee and invitation letter are not refunded and the reasons are usually not explained. However, the most common reasons for visa denial are:
- errors or false information in the documents;
- previous violations of Russian laws during previous visits to Russia;
- outstanding criminal convictions;
- to protect Russia's defense capabilities or public health.
BUSINESS ELECTRONIC VISA (E-VISA)
Russia offers the opportunity to obtain a single-entry business visa in electronic form, valid for up to 30 days.
To apply for an electronic visa, you must fill out an application on the website of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia no earlier than 20 days and no later than 4 days before the planned date of entry into Russia.
No consular fee is required for obtaining an electronic visa, and no invitation or other documents confirming the purpose of the trip are necessary. The processing time for an electronic visa is up to 4 days.
This visa is issued for visiting only one of these regions of Russia: (i) Far Eastern Federal District, (ii) Kaliningrad Oblast, or (iii) the city of St. Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast. An electronic visa issued for visiting one of the listed regions is not valid for visiting other regions of Russia.
The electronic visa is valid for entry and exit from Russia only through certain checkpoints in the visiting region. The allowed period of stay in Russia with such a visa is up to 8 days (including the day of arrival and the day of departure).
Foreigners arriving on electronic visas are required to have valid medical insurance that covers their entire trip in Russia.
Electronic visas are suitable for short-term, one-time business trips to Russia.
After receiving a visa from the consulate or in electronic form, a foreign citizen is entitled to enter Russia from the date specified in the visa as the start of its validity period. Further details are provided regarding the features of obtaining each type of visa.
To obtain a business visa, an invitation to enter Russia must be processed and sent to the foreign citizen in the manner described above. The visa can then be obtained at the consulate.
Insurance necessary to obtain a business visa can be obtained by contacting an insurance company. The cost of such insurance depends on the person's age, insurance program, insurance coverage amount, and the reputation of the insurance company.
Resume:
1. Business and work visas are issued by Russian consulates based on an invitation received from a Company by a foreign citizen.
2. To obtain an invitation to enter Russia, the inviting Company or its partner must register with the immigration service and submit an application for an invitation with a package of documents. For an invitation for a work visa for a foreign worker, a work permit must already be issued.
The migration service sends the electronic invitation by email to the appropriate Russian consulate and to the Company's email address. If the invitation is received on paper, the Company must pass it on to the foreign citizen in the country where the visa will be obtained.
The processing time for such an invitation is up to 20 working days.
For business visas with the purpose of "commercial" and "business" travel, the Company can issue an invitation in a simple written form, on its letterhead. Such an invitation must be given to the foreign citizen for submission to the consulate to obtain a business visa. As practice shows, obtaining a visa based on such an invitation is possible only for a small number of requested visas.
3. To apply for a visa, the foreigner must contact the Russian consulate or visa center in the country where the visa will be obtained with an application, invitation, and relevant package of documents, and pay the consular fee. Usually, for some types of visas, consulates provide expedited processing services for an increased consular fee.
The consulate issues a visa with the parameters specified in the invitation to enter Russia.
4. Russia provides the opportunity to obtain a single-entry business visa in electronic form. The validity period of such a visa is up to 30 days.
To obtain such a visa, it is necessary to fill out an application on the website of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia no earlier than 20 days and no later than 4 days before the intended date of entry into Russia.
...
Features of obtaining a business visa

To obtain a business visa, it is necessary to follow the procedure described above to prepare and send an invitation to the foreign citizen for entry into Russia.
Then, the visa should be obtained at the consulate.
...Features of obtaining a work visa

You will learn:
1. What are the features of obtaining a work visa?
2. What are the peculiarities of obtaining a work visa for highly skilled foreign workers and for regular foreign workers?
Unlike a business visa, the peculiarity of a work visa is that its issuance requires a corresponding invitation and a work permit. To obtain a work permit, a labor contract with the company must be provided. The contract should contain the following special conditions:
- the contract comes into force no earlier than the receipt of the work permit;
- a section with the details of the work permit (to be filled in after its receipt);
- the details of the medical insurance policy (it must already be issued).
It is important to notify the migration service no later than 3 days after signing the employment contract (it can be done on the same day as submitting the documents for the work permit).
After submitting the documents for the work permit, a petition with an acceptance stamp is issued. The original petition must be attached to the documents for obtaining a work visa invitation.
It is important to pay attention to the validity period of the passport: it must be at least 1.5 years from the start date of the work visa.
During the process of obtaining a work permit, the tax service automatically assigns a Russian taxpayer identification number (INN) to the foreign worker based on the migration service data.
For foreign highly skilled workers, it is advisable to provide documents confirming their high qualifications (usually a diploma of higher education).
Refusal to issue the document can occur due to errors in the paperwork, violations of migration legislation, and submission of false information.
Summary:
1. The peculiarity of a work visa is that it requires obtaining a work permit first.
2. When applying for a work visa, the validity of the foreign worker's (non-SME) passport should be at least 1.5 years from the start date of the visa.
При копировании материалов ссылка на сайт Lawspells (www.lawspells.com) обязательна.
How to obtain a work visa for a highly qualified specialist?

You will learn:
1. For how long is a work visa for a highly qualified specialist (HQS) issued?
2. Specifics of obtaining a work permit and invitation for entry into Russia for HQS.
3. Specifics of the procedure for obtaining a work visa for HQS.
HQS are issued a multiple-entry work visa for the purpose of "employment," for the duration of the employment contract but not exceeding 3 years. Such a visa may be repeatedly extended (for the duration of the employment contract with the HQS but not exceeding 3 years for each extension).
Before submitting documents for obtaining a work visa for HQS, it is necessary to obtain a work permit and an invitation for entry into Russia.
OBTAINING A WORK PERMIT FOR HQS
To obtain a work permit for HQS, you need to:
1. Pass an interview with the immigration service to explain the need for hiring a highly qualified specialist in the Company. Although this is not required by law, in practice, immigration officers often require the presence of the Company's CEO at the interview;
2. Prepare a document package and submit it to the immigration service.
The processing time for obtaining a work permit is 14 working days.
It is important to remember that within 3 days after signing an employment contract with a foreign employee, the Company must submit a notification of such a contract to the immigration service.
As a result, the foreign employee (HQS) receives a work permit (a plastic card with his/her information, validity period, and the region(s) where he/she can work).
It is only allowed to work in the Company specified in the work permit. To work in another Company, a new work permit must be obtained.
INVITATION FOR ENTRY TO RUSSIA FOR HQS
Invitation for entry to Russia for HQS is issued in the general manner, however, there are some peculiarities.
The processing time for the invitation in this case is not 20, but 14 working days. In case of facts indicating the urgent need for the HQS to enter Russia and a positive decision of the immigration service management, the processing time can be reduced to 3 days.
GETTING A VISA FOR HQS
After receiving information about the readiness of the work permit and obtaining an invitation for a work visa, the HQS or its authorized representative must submit a visa application to the Russian consulate specified in the invitation. The processing time for a work visa usually depends on the chosen consulate service package (minimum processing time - 1 business day). HQS are issued a single-entry visa valid for up to 3 years.
After the first entry into Russia, the foreign employee (HQS) needs to obtain a work permit from the migration service.
According to Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the remuneration for HQS includes the following: compensation for work, bonuses, various types of compensation (for example, adverse climatic conditions), and additional payments.
Resume:
1. A multiple-entry work visa is issued for the purpose of "employment" for a term of the employment contract, but not exceeding 3 years. Such a visa can be repeatedly extended. To obtain this visa, it is necessary to obtain a work permit and an invitation to enter Russia.
2. In order to obtain a work permit for a foreign worker, it is necessary to pass an interview with the immigration service and submit the necessary package of documents. The processing time for a work permit is 14 business days.
3. An invitation to enter Russia for a foreign worker is issued faster than usual, within a period of not 20, but 14 business days. In certain cases, such a period may be reduced to 3 days.
4. After receiving information about the readiness of the work permit and receiving an invitation for a work visa, the foreign worker or their legal representative submit an application for a visa at the Russian consulate specified in the invitation.
5. After the first entry into Russia, the foreign employee (HQS) must obtain a work permit from the immigration service.
...How to obtain a work visa for a regular foreign employee (non-highly qualified specialist)?

You will learn:
1. What is the duration of a work visa for a regular foreign employee?
2. Features of obtaining a work permit for a regular foreign employee.
3. Features of the procedure for obtaining a work visa for a regular foreign employee.
The employment of regular foreign employees is a more complex and lengthy process than the employment of highly qualified specialists (HQS). After obtaining a work permit, a regular foreign employee is issued a single-entry work visa for a period of up to 3 months. Subsequently, such a visa can be reissued as a multiple-entry visa for up to 12 months.
Unlike HQS, a regular foreign employee requires not only a work permit but also a permit for the company to attract foreign labor. Only after obtaining these permits can an invitation to enter Russia be issued to such an employee and a visa obtained.
Another restriction when hiring a regular foreign worker is the quotas set by Russia. Every year, quotas are set in Russia for the maximum number of foreign workers that companies can hire. Therefore, a company must first submit an application to a special commission, which meets on average once every 3 months. The commission decides on the possibility of allocating a quota to the company for the required number of regular foreign workers. If the annual quota is exhausted at the time of application, the company will not be able to hire such a foreign worker. In the future, quota adjustments (clarifications) may be made, but the chances of obtaining a quota are very low. Therefore, it is advisable to submit applications for quotas for the required number of workers in the middle of the year preceding the year in which the quotas are allocated, when they are not yet exhausted (after their publication).
There is a limited list (no more than 100 positions) of non-quota professions (positions). Workers with such professions can be hired without submitting quota applications. This significantly simplifies the process of obtaining a work permit.
GETTING A WORK PERMIT FOR A REGULAR FOREIGN WORKER
As can be seen from the described actions, the process of hiring a regular foreign worker is quite laborious.
To obtain a work permit for a regular foreign worker, it is necessary to:
1. Before starting the process of obtaining a work permit for a regular foreign worker, the company needs to register with the migration service and obtain permission for the company to attract foreign workers.
2. If the profession (position) is quota-based, the company first needs to submit a quota application to the relevant commission. If the commission has allocated a quota to the company for this worker, the process of hiring can be continued.
If the profession is non-quota, this step can be skipped.
3. Post a job vacancy on behalf of the Company at the Employment Center for the position and profession for which an ordinary foreign worker needs to be hired. If the Employment Center has suitable Russian candidates for the vacancy, they may be referred to the Company for an interview. The Company must conduct an interview and provide a motivated refusal to hire each candidate if it does not wish to employ them.
After 30 days from the date of posting the vacancy, if no Russian candidate has been hired for the position, the Company may proceed with the process of hiring a foreign worker.
4. Submit a package of documents to the migration service for obtaining a work permit for the ordinary foreign worker.
5. The foreign worker must undergo testing for knowledge of the Russian language, the basics of Russian history and legislation, as well as undergo a medical examination and provide medical tests for the absence of diseases (HIV, tuberculosis, etc.).
6. Submit documents to the migration service for obtaining an invitation for the foreign worker to enter Russia on a work visa. The processing time for such an invitation is 20 working days.
On average, the processing time for obtaining a work permit and work visa for a foreign worker is 3.5 months if the profession (position) is not subject to quotas. If the profession (position) is subject to quotas and the Company needs to obtain a quota, the processing time may take a few more months (around 5 months).
Within 3 days after signing a labor contract with a foreign worker, the Company is obliged to notify the migration service of the conclusion of such a labor contract. As a result, the foreign worker receives a work permit (a plastic card with their information, validity period, and region in which they can work).
It is only possible to work under the permit in the company specified in the work permit. To work in another company, a new work permit must be obtained.
OBTAINING A VISA FOR A REGULAR FOREIGN WORKER
After receiving information about the readiness of the work permit and an invitation for a work visa, the foreign worker or their legal representative must apply for a visa at the Russian consulate indicated in the invitation. The processing time for a work visa usually depends on the chosen consulate service tariff (minimum processing time is 1 business day). The foreign worker is initially issued a single-entry visa valid for 3 months.
After the first entry into Russia on a single-entry visa, the worker needs to obtain a work permit from the migration service and submit documents to extend the visa validity period up to 12 months.
Do not agree to tempting offers found on the Internet and purchase a work invitation to Russia. Without concluding a labor contract with a Russian employer immediately after entering Russia, the short-term work visa for the foreigner simply will not be extended, and the money paid for such an invitation will be wasted.
Resume:
1. A multiple-entry work visa for up to 12 months is issued to a regular foreign worker for the purpose of "employment" upon obtaining a permit to attract foreign labor for the Company, a work permit, and an invitation to enter Russia for the foreign worker. In some cases, the Company needs to obtain a quota from the state for the required number of regular foreign workers.
2. To obtain a work permit for a regular foreign worker, it is necessary to:
- register the Company with the migration service and obtain a permit to attract foreign labor;
- apply for a quota in the quota commission (if the position is quota-based);
- advertise the vacancy on behalf of the Company at the Employment Center for 30 days;
- submit a package of documents to the migration service for the issuance of a work permit for a regular foreign worker;
- the foreign worker must pass a test on knowledge of the Russian language, the basics of the history and legislation of Russia, as well as undergo a medical examination and tests for diseases (HIV, tuberculosis, etc.);
- submit documents to the migration service for the issuance of an invitation for the foreign worker to enter Russia on a work visa.
On average, the processing time for obtaining a work permit and work visa for a foreign worker is 3.5 months if the profession (position) is non-quota. If the profession (position) is quota-based, the processing time may take longer (about 5 months).
3. After receiving information about the readiness of the work permit and obtaining an invitation for a work visa, the foreign worker or their authorized representative submits an application for a visa to the Russian consulate specified in the invitation.
Initially, the foreign worker is issued a single-entry visa valid for 3 months. After the first entry into Russia with a single-entry visa and obtaining a work permit, the work visa can be extended for a period of up to 1 year.
...
Entry, stay and exit from the territory of Russia. What needs to be done upon entry into Russia?

You will learn:
1. First steps upon the entry of a foreigner into Russia. How to fill out a migration card and how to register at the place of stay?
MIGRATION CARD
Upon entry into Russia, a foreign citizen must receive and fill out a migration card, which is provided free of charge by representatives of the carrier (train personnel, airline personnel, maritime and river vessels, etc.).
The migration card form is filled out in Russian. However, if the foreigner does not speak Russian, it is allowed to fill out information about oneself in Latin letters in accordance with the data specified in the passport.
When passing through the Russian border checkpoint, part of the migration card remains with the border officials, and the second part is returned to the foreigner. On the reverse side of the migration card, border officials must put a stamp indicating entry into Russia.
The foreign citizen must always have the original migration card with him/her and not give it to anyone until leaving Russia. It is advisable to insert such a migration card into the passport, as it may be requested by police officers in Russia or at the border control when leaving the country.
The document cannot be laminated.
In case of damage or loss of the migration card, the foreigner must immediately report this to the nearest migration service office and obtain a duplicate. In this case, it is necessary to present the passport with the visa on the basis of which he/she entered Russia. A duplicate migration card is issued free of charge.
REGISTRATION AT PLACE OF RESIDENCE
After arriving in Russia, a foreign citizen must be registered at the local migration service office according to their place of stay. This registration must be done within 7 business days. Members of the diplomatic corps and their accompanying family members can register within 90 days.
If a foreign citizen resides in a hotel, the hotel staff must register them at the place of stay. If an apartment is rented for a foreigner, the owner of the apartment must provide the registration, for which they need to be given copies of the passport with visa and migration card.
In any case, after registration, the original form with the migration service stamp must be handed over to the foreigner.
When changing the place of stay (moving to another apartment, hotel, or city), a new registration must be completed.
If the hotel staff or apartment owner refuses to carry out the registration, the foreigner must immediately inform the responsible employee of the company. In case of violation of the requirements of Russian migration laws, the company may be fined a substantial amount and the foreigner may face a ban on entering Russia in the future in addition to the fine.
Until departure from Russia, it is necessary to keep the migration card and the original registration form. They can be checked by both Russian police officers and border control when leaving Russia. Registration may also be required for presentation in various Russian institutions, such as a notary office.
Currently, foreign citizens must provide a negative COVID-19 test taken no later than 72 hours before arriving in Russia. Quarantine and self-isolation must be observed until test results are received. Administrative fines and punishments are provided for violations of these requirements.
Resume:
1. When entering Russia, a foreigner is required to obtain and fill out a migration card, which is provided free of charge by the staff of trains, planes, sea and river vessels. When crossing the Russian border, part of the migration card is left with the border guards, and the second part with the entry stamp is returned to the foreigner.
The foreigner must have the original migration card with them, as the police may request it for verification. In case of damage or loss of the migration card, the foreigner is obliged to promptly obtain a duplicate.
2. After arriving in Russia, a foreigner must be registered at their place of stay (in a hotel or apartment) at the local migration service office. Such registration must be done within 7 working days. HQS and their accompanying family members can register within 90 days.
After registration, the foreigner is issued an original registration form with a stamp from the migration service, which they must have with them. The police and border service (when leaving Russia) may also check this form.
...
What to consider for foreign citizens in Russia?

You will learn:
1. In which part of Russia and for how long is a foreign citizen entitled to stay and work?
2. Who provides medical care and insurance to a foreigner?
3. In what cases can a foreign citizen be deported from Russia?
4. What bans and restrictions should be primarily considered to avoid problems with the Russian police?
STAYING IN RUSSIA
Foreign citizens have the right to free movement for personal or business purposes within Russia, based on documents issued for entry into Russia.
Exceptions include visiting territories, organizations, and facilities that require special permission for entry (e.g. military objects, border zone, state institutions working with state secrets).
Foreign workers can work only in the territory specified in the work permit, except in cases where:
- A foreign worker belongs to the list of professions established by the Ministry of Health of Russia (for example, bricklayer, boatswain), managers of companies and divisions sent on business trips, but not exceeding 10 calendar days during the validity period of the work permit. For Highly Qualified Specialists (HQS), this limitation is not 10 but 30 days per year.
- The work is carried out by a regular foreign worker on the go or has a traveling nature, and this is determined by his employment contract. Such work can be carried out for no more than 60 calendar days during the validity period of the work permit. This time limit does not apply to HQS.
The company, when applying for a visa invitation, provides guarantees of medical care for the foreign citizen. When applying for a work visa, providing a copy of the medical insurance policy is mandatory. If necessary, the foreign citizen has the right to count on free emergency medical care. In other cases, he needs medical insurance, and if that is not enough, the company is obliged to cover the costs of medical services.
The law establishes serious responsibility for the company for the invited foreign citizen, therefore it is necessary to monitor his compliance with migration laws throughout his stay in Russia.
A foreign citizen may be fined or expelled from Russia (with a ban on entry for 3 years) in the following cases:
- The foreigner violated the procedure for crossing the Russian border;
- The foreigner did not register in a timely manner at the place of stay;
- The foreigner does not have documents confirming the right to stay in Russia (visa, work permit (for foreign workers), migration card, registration form at the place of stay), or when such documents are lost and no statement has been made to the police about their loss;
- The purpose of the trip specified in the visa does not correspond to the activity that the foreigner actually performs during their stay in Russia;
- The foreigner provided false information about themselves when applying for entry documents to Russia;
- The foreigner avoids leaving Russia after the visa has expired.
To avoid problems related to the violation of Russian migration laws and to have the opportunity to visit Russia in the future, a foreign citizen needs to: (i) provide accurate information about themselves when applying for entry documents, (ii) complete all formalities upon arrival in Russia within the specified time frame, (iii) have all documents confirming the legality of their stay in Russia, (iv) engage in the activity specified as the purpose of their visit in the visa, and leave Russia upon the expiration of the visa.
PROHIBITIONS TO BE AWARE OF
To avoid problems with the Russian police, it is important to pay attention to certain prohibitions that carry administrative penalties. In Russia, it is prohibited to:
- smoke, consume alcoholic beverages and be in a state of intoxication in public places (such as parks, restaurants, public transport, children's playgrounds, airports, etc.);
- sell alcohol during nighttime hours. Each region independently determines this period, usually from 23:00 to 10:00;
- possess, purchase, sell, or use any narcotics in any amount;
- use profanity in public places;
- make noise (talk loudly, shout, play music, perform repair work, etc.) both outside and at home after 23:00;
- engage in entrepreneurial activities without a special permit.
RESTRICTIONS TO PAY ATTENTION TO
Foreigners in Russia face certain restrictions related to civil rights of Russian citizens. Thus, foreign citizens in Russia:
- do not have the right to vote or be elected, participate in referendums;
- cannot work in government service;
- do not have the right to participate in the administration of justice;
- are not allowed to create political parties or be their members.
The main rules for the stay of foreign citizens in the Russian Federation consist of timely informing migration authorities and obtaining the necessary documents granting the right to permanent or temporary residence in Russia. Without them, it is impossible to engage in employment and live in the country on legal grounds.
Resume:
1. Foreign citizens have the right to freedom of movement for personal or business purposes throughout Russia, except for territories that require special permission to enter (such as military facilities). However, foreigners are only allowed to work in the territory specified in their work permit, with exceptions for business trips lasting no more than 10 calendar days during the validity period of the work permit. For foreign workers employed in the aviation industry, such limitation is 30 calendar days per year. Foreigners can also work while travelling or in a mobile capacity as specified in their employment contract, with a maximum period of 60 calendar days during the validity period of the work permit, or unlimited for those employed in the aviation industry.
2. When applying for a visa invitation and work permit, the company provides guarantees of medical insurance for the foreigner. Foreign citizens are entitled to free emergency medical care in Russia, but otherwise, they need to have medical insurance. The company is obliged to cover the costs of medical services provided to the foreigner if the insurance is insufficient.
3. Foreigners can be fined or deported from Russia with a ban on entry for 3 years for violating migration legislation (e.g. failure to register their place of residence), providing false information when applying for migration documents, or violating other provisions of Russian legislation.
4. To avoid problems with the Russian police, foreigners should first and foremost not violate everyday administrative restrictions that are established for Russian citizens in the areas of behavior in public places, trade, alcohol and drug consumption, and entrepreneurial activities. There are also restrictions in Russia that apply only to foreign citizens, such as prohibition to work in public service and right to vote in elections, among others.
При копировании материалов ссылка на сайт Lawspells (www.lawspells.com) обязательна.
What foreigners need to consider when leaving Russia?

You will learn:
1. When must a foreigner leave Russia?
2. What documents can be checked by foreign citizens when leaving Russia?
3. In what cases can leaving Russia for a foreign citizen be restricted?
4. What should be done if the company doubts that the foreign citizen will fulfill their obligation to leave Russia?
As the inviting party, the company is obliged to ensure the timely departure of the foreign citizen from the territory of Russia no later than the expiration of their visa. If there are objective reasons that prevent the foreign citizen from leaving Russia (lack of money, loss or damage of documents, illness, etc.), the company is obliged to assist in the elimination of these reasons.
When leaving, foreigners must have the original migration card and the original registration form for their place of residence to present them when crossing the Russian border. These documents are not checked in 100% of cases, however, in their absence, immigration authorities are formally entitled to hold the foreign citizen responsible for violating Russian immigration laws.
Departure from Russia may be restricted to a foreign citizen in cases where:
- They are detained on suspicion of, or charged with, committing a crime until a decision is made on their case or until the sentence of the court enters into legal force;
- They are convicted of committing a crime on the territory of Russia until the sentence is served or until they are released from punishment;
- They evade fulfilling obligations imposed on them by the court until the obligations are fulfilled or until an agreement is reached with the party to whom such obligations exist;
- They have not fulfilled tax obligations until these obligations are fulfilled;
- They are held liable for committing an administrative offense on the territory of Russia until the punishment is served or until they are released from punishment.
If there is a conflict between a company and a foreign citizen, in any case, if there are grounds to believe that they will not fulfill their obligations to leave the country in a timely manner, to avoid the company being held responsible, it is necessary to personally hand the foreigner (if this is not possible - send by mail with a description of the attachment and notification of delivery to the address of their residence) a written reminder of the need to leave Russia. It is advisable to do this in advance, at least 10 days before the expiration date of their visa.
Quite often, foreign citizens do not receive notifications from the relevant authorities about the prohibition of leaving Russia. However, if you have not received this order, it does not mean that it does not exist in reality. Before buying tickets and planning a trip abroad, it is recommended to independently check for any restrictions. This process can be done online. All the necessary information can be found on such websites as the Federal Bailiff Service, the government services website, and the Federal Tax Service. In addition, you can contact these agencies directly and obtain information from their employees.
Resume:
1. Foreign nationals are required to leave Russia before their visa expires.
2. In addition to the passport with a visa, a foreign national must have the original migration card and the original registration form at the place of stay when leaving.
3. The departure of a foreign national from Russia may be restricted if they have been convicted of a criminal or administrative offense or have not paid necessary taxes.
4. The company is obliged to ensure the possibility of a foreign national leaving Russia. In case it is impossible due to the foreign national's lack of conscientiousness and violation of their obligation to leave Russia, the company must provide a written reminder to the foreign citizen about the need to leave, which will further minimize the risks of the company being held responsible for violating migration legislation.
...
Responsibility for violation of migration laws in Russia

You will learn:
1. What types of liability and from what point in time can be applied for violation of the migration legislation of Russia?
2. Who can be held responsible for violation of the migration legislation of Russia?
3. The most common types of violations for which responsibility is imposed for violation of the migration legislation of Russia.
From the moment a foreigner crosses the Russian border, the Russian laws apply to him and the inviting party, which must be strictly observed. In Russia, serious measures of liability are established for violations of migration rules. The company, its management, employees, and the foreign citizen himself may be subject to administrative and criminal liability.
In practice, many companies disregard this responsibility, not realizing the real risks to their business. This is mainly because at the moment the supervisory authorities of Russia cannot physically hold all violators responsible. State control does not yet cover all companies, foreign citizens, and their violations. However, according to statistics from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia, hundreds of thousands of events are held annually to identify violations of migration laws, planned and unscheduled inspections of companies. Thousands of companies and hundreds of thousands of foreign citizens are held accountable. Moreover, not only the receiving party and the foreigner, but also companies and citizens providing any services or assistance to a foreigner who violates Russian migration legislation can be held responsible.
The maximum criminal liability provides for 7 years of imprisonment. Administrative liability, on the other hand, provides for significant fines, prohibitions, and applies to violations against each foreigner individually. This means that in the event of any violation, for example, in relation to 3 foreign citizens, the Company and/or its CEO may be fined threefold.
In addition to the application of criminal and administrative liability, a foreigner may be prohibited from entering Russia for violation of immigration legislation. Such a ban occurs if the foreigner has been repeatedly held administratively liable in Russia within 3 years. The entry ban will be in effect for 3 years from the date the foreigner was held responsible.
The most common violations for which companies and foreigners are held liable include:
- Violation of entry rules into Russia or residence regime, failure to notify the migration service of their place of residence;
- Lack of documents confirming the right to stay in Russia (migration card, visa, etc.), and in case of loss of such documents - failure to notify the migration service of their loss;
- Evading departure from Russia upon the expiry of the visa;
- Non-compliance of the stated purpose of entry into Russia with the actual activities carried out;
- Provision of housing, transportation or any other services to a foreigner staying in Russia in violation of the residency regulations;
- Company's failure to timely notify the migration service of the arrival or departure of a foreign citizen for the purposes of their migration registration;
- Foreigner working in Russia without a work permit and hiring such a foreigner to work;
- Failure to notify about the conclusion or termination of a labor contract or service contract with a foreigner within the time period specified by law;
- Company's non-compliance with the restrictions imposed on foreigners for carrying out certain types of activities;
- Provision of false information about a foreigner or submission of forged documents by the receiving party.
It should be remembered that responsibility for violations in the migration sphere is closely related to responsibility for violations of labor legislation. Thus, during inspections of companies for violations of labor laws, compliance with migration legislation in relation to the company's employees is also checked. Often, violations in one sphere of legislation help to identify violations in another and also to hold the company, employees, and foreigners accountable for violations in both areas of legislation.
Next, specific types of responsibility for violating Russian migration laws are considered. If a foreigner does not have documents, he or she will be taken to a Temporary Detention Center for Foreign Citizens. It is desirable for the migrant to be deported back to his or her homeland as soon as possible. For this, he or she needs to tell the truth about himself or herself. Administrative and criminal liability is applied for violation of migration law. Due to changes in the law on the registration of migrants by actual place of residence, new articles have appeared in the Criminal Code.
Summary:
1. Administrative and criminal liability is applied for violation of Russian migration legislation.
2. Administrative liability provides for significant fines, restrictions and is imposed for violations in relation to each foreigner individually.
If a foreigner has been repeatedly (more than 2 times) held administratively liable in Russia within 3 years, he may be banned from entering Russia for 3 years.
The maximum criminal liability for violating migration legislation provides for 7 years of imprisonment.
3. Liability may be imposed on the foreign citizen himself, the Company, the partner involved by the Company, providing entry for the foreign citizen (through the leader and employees of the Company and partner), as well as companies and individuals providing any services or assistance to a foreigner who violates Russian migration legislation.
4. The most common violations of migration legislation for which liability is applied include: absence of necessary migration documents for a business trip or work in Russia, provision of false information about the foreigner and the purpose of his trip, failure to comply with obligations on necessary notifications to state authorities, provision of transport, housing and services to a foreigner who violates Russia's migration laws, etc.
...What administrative responsibility is provided for a company, its management, and employees?

You will learn:
1. Categories of violations of Russian migration legislation for which administrative responsibility is applied.
2. Types of administrative responsibility and fines for violating migration legislation.
Violation of migration laws in Russia can result in serious responsibility for a company and its employees. Such responsibility is divided into several areas where violations occur.
|
Violation |
Penalties |
|
Migration registration Failure to fulfill obligations for migration registration in cases where the violation is not serious enough for criminal liability. The obligations for migration registration include: notifying the migration service of the arrival/departure of a foreign citizen. |
- Fine for company employees - 40,000 - 50,000 rubles; - Fine for the company - 400,000 - 500,000 rubles. |
|
Housing and Medical Care If the company fails to provide financial, medical, and housing assistance to the foreigner during their stay in Russia. |
|
|
Purpose of entry and exit from Russia If the Company fails to ensure that (i) the activity that the foreigner actually carries out in Russia corresponds to the purpose of the trip specified in the visa; and (ii) the foreigner leaves Russia in a timely manner upon the expiration of the visa. |
- Fine for Company employees - 45,000 - 50,000 rubles; - Fine for the Company - 400,000 - 500,000 rubles. |
|
False information If the Company provided false information about the purpose of the foreigner's trip to Russia when processing their entry documents. |
|
|
Hiring for work |
|
|
Hiring a foreigner: - if they do not have a work permit; - for a profession (specialty, position) not specified in the work permit; - outside the region of Russia where the work permit was issued. |
- Fine on company employees - 25,000 - 50,000 rubles; - Fine on the company - 250,000 - 800,000 rubles or suspension of company operations for a period of 14 to 90 days; For the same violations in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Moscow and Leningrad regions of Russia, increased fines are applied: - Fine on company employees - 35,000 - 70,000 rubles; - Fine on the company - 400,000 - 1,000,000 rubles or suspension of company operations for a period of 14 to 90 days. |
|
Hiring a regular foreign worker without obtaining permission from the Company to attract and use foreign workers. |
|
|
Failure to notify or violation of the procedure or form of notification of the migration service about the conclusion or termination of an employment contract with a foreigner. |
- Fine for Company employees: 25,000-50,000 rubles; - Fine for Company: 250,000-800,000 rubles or suspension of Company's activities for a period of 14 to 90 days; For the same violation in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Moscow and Leningrad regions of Russia, increased fines apply: - Fine for Company employees: 35,000-70,000 rubles; - Fine for Company: 400,000-1,000,000 rubles or suspension of Company's activities for a period of 14 to 90 days. |
|
Violation by a foreign citizen of the deadline for applying for changes to the information contained in the work permit, or failure to apply for such changes. |
- Fine for the foreign worker - 4,000-5,000 rubles. |
As can be seen from the above-mentioned fines, for each violation of migration laws, the minimum and maximum administrative liability for employees and the head of the company is 25,000 and 70,000 rubles, respectively, and for the company - 250,000 - 1,000,000 rubles.
As a rule, within the framework of business migration, companies invite more than one foreigner for a business visit or to work in Russia, and when implementing large projects that involve a large migration flow, the risks of the company increase exponentially.
A suspension of activity for up to 90 days can be fatal for a company. In addition to the possibility of losing business during this period, such a measure of responsibility, like any other type of responsibility in this area, does not bode well for the company in the future. The company will subsequently be under close scrutiny of regulatory bodies.
As mentioned above, repeated imposition of responsibility on the head of the company may be the reason for a ban on entry to Russia for 3 years, which can also be devastating for the company's business in cases where its business directly depends on the presence of such a leader in Russia.
The company's adoption of measures to prevent administrative liability and the ability to defend its position in cases where regulatory bodies illegally impose punishment is much more beneficial than bearing the consequences of such liability.
It is important to remember that the ultimate responsibility for the proper conduct of business lies not with the chief accountant, but with the company's leader. In case of questions from regulators, all claims are addressed to the company and its head personally.
Resume:
1. Administrative liability for violating Russian migration legislation is applied for violations in the field of migration registration, obligations to provide foreigners with housing and medical care, compliance of the purpose of the foreigner's entry into Russia with his actual activities, and subsequent fulfillment of the obligation to leave Russia, providing false information about a foreigner, and violation of rules when hiring foreign specialists for work.
2. Administrative liability for violation of migration laws is imposed in the form of fines on companies, their employees, foreigners, and citizens illegally assisting them, as well as suspension of companies' activities. The minimum and maximum administrative liability for employees and the manager of the Company and its partner, as well as other companies and citizens who assist a foreigner in violating migration legislation, is 25,000 to 70,000 rubles for individuals and 250,000 to 1,000,000 rubles for legal entities for each violation.
A significant measure of responsibility for companies can be the suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
A foreigner may be prohibited from entering Russia for 3 years.
...What administrative responsibility is provided for a foreign citizen?

You will learn:
1. Types of administrative offenses committed by foreigners and the corresponding responsibility applied to them.
Foreign citizens who violate the rules of entry and stay in Russia bear administrative responsibility. The following foreign citizens are recognized as illegally staying in Russia and are responsible according to its legislation:
- those who arrived in Russia in violation of the procedure for crossing the state border;
- those who did not register at the place of stay in a timely manner;
- those who avoided leaving Russia after the expiration of the permitted stay period;
- those who provided incorrect or false information during migration registration.
Violation of the rules of entry into Russia or the stay regime, including:
- absence of documents confirming the right to stay in Russia;
- loss of such documents and failure to apply for their loss to the relevant authority;
- inconsistency of the declared purpose of entry into Russia with the actual activity carried out during the period of stay;
- evasion of leaving Russia after the expiration of the permitted stay period entails a fine of 2,000 to 5,000 rubles (in Moscow, St. Petersburg, Moscow and Leningrad regions - 5,000 to 7,000 rubles) with deportation outside of Russia or without it.
In case a foreigner is brought to administrative responsibility for violating Russian legislation more than twice, he may be prohibited from entering Russia for 3 years.
In conclusion, it can be said that the system of legal norms regulating issues of bringing foreign citizens to responsibility, as well as the mechanism for implementing these norms in the legislation of our country, is well-developed and generally does not differ from the mechanism for bringing Russian citizens and other subjects of administrative jurisdiction to administrative responsibility.
Summary:
1. Administrative responsibility applies to foreigners for violations of entry and stay rules in Russia.
2. The maximum administrative responsibility for violating Russian migration legislation for a foreigner is up to 7,000 rubles with expulsion from Russia.
...
What is the criminal liability for violation of migration laws in Russia?

You will learn:
1. Categories of violations of Russian migration legislation for which criminal liability is applied.
2. Types of criminal liability for violation of migration legislation.
Criminal liability for violation of Russian migration legislation is provided for organizing the illegal entry of foreigners into Russia, their illegal stay or illegal transit passage, as well as for fictitious registration of foreigners at a place of residence in a residential premises or at a place of stay. The place of stay refers to a residential premises in which a foreigner is temporarily located, and the place of residence refers to a premises where a foreigner permanently resides or in accordance with a permit for temporary residence.
Violations related to fictitious registration of foreigners at the place of residence or stay are punishable by:
- A fine of 100,000 to 500,000 rubles;
- or an amount equivalent to the convicted person's salary or other income for a period of up to 3 years;
- or forced labor for up to 3 years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for up to 3 years or without such deprivation;
- or imprisonment for up to 3 years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for up to 3 years or without such deprivation.
Fictitious registration of foreign citizens at the place of stay in Russia means:
- registration based on false information or documents;
- registration of foreign citizens at a residence without their intention to actually live there or without the intention of the hosting party to provide them with that residence for actual living;
- registration of foreigners at an address of a company where they do not work or engage in any other activity.
Along with property owners, the responsibility for illegal registration can also fall on a migration service employee who registered a foreigner based on knowingly false information and documents.
When implementing projects requiring the arrival of a large number of foreign citizens in Russia, even a small mistake in the registration or organization of their stay can lead to charges of organizing illegal migration, which is considered a criminal offense.
The maximum liability under the Russian Criminal Code is provided for the organization of illegal entry of foreigners into Russia, their illegal stay, or illegal transit passage. In this case, there is a risk of punishment in the form of imprisonment for up to 5 years with restriction of liberty for up to 2 years or without it, or up to 7 years with a fine of up to 500,000 rubles (if the crime is committed by a group of persons by prior conspiracy or an organized group).
Even administrative offenses, if committed two or more times in the last 2 years, are grounds for refusal of entry into the country. The same situation applies to criminal offenses. So, if a person has a repeat conviction (regardless of whether it is Russian or from their home country), they may be restricted from entering the country and may also be deported.
Summary:
1. Criminal liability for violating Russian migration laws applies to:
- organizing illegal entry of foreigners into Russia, their illegal stay, or illegal transit passage;
- fictitious registration of foreigners at the place of residence in a residential premises or at the place of stay.
2. Criminal liability for violating migration laws can result in fines, restrictions or deprivation of freedom, deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities. The maximum criminal liability can be imprisonment for up to 5 years with restriction of freedom for up to 2 years, or imprisonment for up to 7 years with a fine of up to 500,000 rubles (if the crime is committed by a group of people).
...
How to avoid liability for violating migration laws in Russia?

You will learn:
1. Recommendations for reducing the risks of liability for the company when organizing business migration.
Given the seriousness of the liability for violating Russian migration legislation, it is necessary to correctly plan and organize all processes related to migration from the very beginning. In this case, preventive measures, despite the costs and efforts, are always more profitable than the possible liability, legal, and financial consequences it entails.
For large projects, a preliminary calculation of all processes and identification of risky/controversial points related to foreign citizens is considered mandatory. And in many cases, to provide the company with "insurance against incorrect/double interpretation of the law by government officials," obtaining official explanations from regulatory bodies is simply necessary.
One of the most obvious ways to minimize risks is to have the correct corporate structure, namely, building a group of companies in such a way as to distribute migration risks among the necessary companies.
Accordingly, with the correct approach to the corporate structure, the claims of regulatory bodies are unlikely to affect the operations of the company itself and the implementation of its projects. Migration risks can be partially shifted to partners (service providers) attracted to organize migration processes for the company. In this case, the risk of project stoppage due to claims of regulatory bodies is significantly reduced.
As practice shows, to successfully implement migration processes and ensure proper functioning of the Company, it is necessary to engage partners - specialized consultants with extensive practical experience. This will not only help to structure the work of the Company with foreign nationals effectively and identify associated risks in a timely manner, but also increase the chances of timely issuance of necessary documents for foreign nationals' entry into Russia, other migration processes, as well as successful resolution of disputes in case of claims by regulatory authorities (who often hold companies responsible unjustifiably or misinterpret legal norms).
Special attention should be paid to the fact that the inviting or receiving party, as well as the officials of the legal entity that provides services to foreign nationals or stateless persons, bear responsibility for violation of the rules of stay in the Russian Federation by foreign nationals and stateless persons.
Resume:
1. To avoid risks of serious liability, it is necessary to pay attention to the proper organization of migration flows within the Company before their implementation, especially for large projects.
2. Proper corporate structuring that considers potential migration risks and the involvement of specialized partners will significantly reduce risks for the Company's operations, including in cases where liability has already been incurred for violating migration legislation.
...
Risks of Business Migration to Russia

You will learn:
1. Types of risks associated with violating Russian migration legislation.
The risks for a company resulting from violations of migration legislation in Russia can be conditionally divided into the following groups:
Organizational - risks at the stage of preparing documents for entry into Russia and their consideration by state authorities. They include both technical errors and, most importantly, improper and untimely settlement of issues with state authorities.
The main organizational risk is failure to obtain documents for the entry of a foreign citizen.
Current - risks during the entire period of stay of a foreign citizen in Russia.
As a rule, they result from:
- incorrect registration of entry documents for a foreigner (for example, the visa indicates the wrong purpose of entry, which is punishable by a fine of up to 400,000 rubles and deportation of the foreigner);
- or violations during the stay of the foreigner in Russia (for example: failure to ensure departure from Russia, which is punishable by a fine of up to 500,000 rubles, or a fictitious registration, which is punishable by up to 3 years of imprisonment).
The main current risk is the receipt of significant fines or even criminal punishment.
Future risks are those that arise after a foreign citizen has left Russia or are somehow related to violations of migration legislation that have not yet been prosecuted. Such risks arise after a regular check by government agencies due to the incompetent application of the law and document processing, both for the entry of foreigners into Russia and during their stay in Russia (for example, registration of a foreign citizen as a new General Director before he or she obtains permission to work in Russia - a fine of 400,000 to 1,000,000 rubles or suspension of the company's activities for up to 90 days). The main future risk is serious financial penalties that can significantly hinder the company's operations.
International business migration is a way to move to a new level of income. There are risks and dangers associated with it, but potentially international business is less dependent on local problems, and therefore more stable in a strategic sense. If you think of your business as a long-term and profitable project, then international business migration and a properly constructed structure will become very useful tools for you.
Summary:
The risks for violating Russia's migration legislation can be conditionally divided into:
- Organizational risks, related to document preparation and their review by government authorities;
- Current risks, usually associated with the consequences of violations upon entry into Russia or violations of Russian legislation during a foreigner's stay in Russia;
- Future risks, related to violations of migration legislation that have already occurred but for which no responsibility has been imposed yet.
...
State regulation of migration in special situations

You will learn:
1. In what cases can the state establish special rules for regulating migration?
2. Recommendations for organizing migration flows of a company in special situations.
In special situations, Russia establishes special rules and restrictions for migration flows. The most significant of such special situations in the near future was the global pandemic that spread the COVID-19 coronavirus infection. Migration flows between countries of the world have become a means of spreading the infection.
The Russian government and president have established special restrictions on the entry and stay of foreigners in Russia, in particular, the entry of foreigners on certain types of visas was prohibited. Migration flows were significantly reduced, and the process of entry for foreigners on allowed types of visas became more complicated.
Thus, to ensure the entry of foreign technical specialists entering Russia for "technical maintenance", the company must first include such specialists in a special list sent to the FSB and migration service. To do this, the company must contact the relevant ministry of Russia, which sends such lists to the FSB and migration service. Only after including specialists in such lists is it possible to obtain an invitation for their entry into Russia and subsequent visa issuance.
In order to timely and effectively resolve the issues of the entry and stay of foreigners for the company in a special situation when the state establishes special restrictions, it is necessary to involve partners (migration service providers) specializing in solving such issues. Partners with the necessary experience are capable of ensuring the company's legal organization of migration flows necessary to ensure its operational activities.
The legal basis of the concept of regulating migration processes in Russia consists of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal laws and other regulatory legal acts, as well as generally recognized principles and norms of international law.
Resume:
1. In special cases, the government establishes special restrictions and regulations for regulating migration flows. For example, such rules and restrictions were established in connection with the COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic.
2. To effectively address issues related to the entry and stay of foreigners in special situations, it is necessary to engage specialized partners with the necessary experience. Such partners can help the company ensure a lawful organization of the necessary migration flows.
...
What is Russia's migration policy? What are its goals?

In accordance with the Constitution of Russia, foreign citizens and stateless persons enjoy rights and bear obligations on an equal footing with Russian citizens, except in cases established by law or international treaty.
The goal of migration policy is to create a situation that contributes to solving problems in the field of socio-economic, spatial, and demographic development of the country, improving the quality of life of its population, ensuring the security of the state, protecting the national labor market, maintaining interethnic and interreligious peace and harmony in Russian society.
Improving Russia's migration legislation involves, first and foremost, establishing simple, understandable, and enforceable rules that correspond to the goals, principles, and tasks of migration policy, free from administrative barriers and the costs associated with them.
Therefore, each state carefully develops all provisions of its migration policy, which provides not only benefits for the country as a whole, but also for the entire population.
Summary:
1. In Russia, foreigners enjoy the same rights and bear the same responsibilities as Russian citizens, except for limitations or preferences established by Russian legislation or international treaties.
...
What are the main laws regulating business migration in Russia?

The legal status of a foreign citizen in the Russian Federation is determined by the following main regulatory legal acts and other subordinate acts:
- Federal Law of August 15, 1996 No. 114-FZ "On the Procedure for Exiting and Entering the Russian Federation";
- Federal Law of July 25, 2002 No. 115-FZ "On the Legal Status of Foreign Citizens in the Russian Federation";
- Federal Law of July 18, 2006 No. 109-FZ "On Migration Registration of Foreign Citizens and Stateless Persons in the Russian Federation".
A foreign citizen legally staying in Russia is a person who has a valid residence permit, or temporary residence permit, or visa and/or migration card, or other documents confirming the foreign citizen's right to stay in the Russian Federation.
Legislation in the field of migration is constantly being updated. The policy in this area is not fully formed and is constantly adapting to changing conditions. The improvement of legislation contributes to the stabilization of migration policy. The successful solution of these issues depends on the economic, political, and social stability of the country.
Summary:
1. The main laws regulating migration in Russia are: (i) "On the Procedure for Exiting Russia", (ii) "On the Legal Status of Foreigners in Russia", and (iii) "On Migration Registration of Foreigners in Russia".
...
Resume

The above information in this guide allows you to identify and implement in the Company's work the basic rules that are recommended to follow to overcome the difficulties of migration processes and avoid serious responsibility for violating migration legislation:
1. It is important to pay close attention to the preparation of documents for the entry of a foreign citizen and to determine in advance what the Company and the foreigner are required to do during his/her stay in Russia and after departure.
2. It is necessary to ensure the competence and proper understanding of the employees responsible for this issue regarding the importance of correctly organizing the entire process of foreign nationals' migration to Russia. Often, serious liability for violation of migration laws is a consequence of incompetent work or negligent attitude on the part of the company's employees responsible for this process.
3. It is recommended to have a reliable and trustworthy partner who can provide professional assistance and protection to the Company in organizing the migration process at any stage and help solve any issues that arise.
The implementation of these rules in the Company's work, proper and timely elaboration of migration issues will allow to reduce or completely eliminate the risks associated with liability for violation of migration legislation.
Specialists of Lawspells law firm have many years of practical experience in the field of migration law. You will find in us a partner who will provide professional assistance and protection in organizing the migration process.
+7-800-5555-970
www.lawspells.com
...
При копировании материалов ссылка на сайт Lawspells (www.lawspells.com) обязательна.